Detecting Trojan and Worm with Capsa Network Analyzer
Trojan and Worms are two major threats to network security. Do you know what exact is a Trojan horse? In Wikipedia, Trojan horses are designed to allow a hacker remote access to a target computer system. Once a Trojan horse has been installed on a target computer system, it is possible for a hacker to access it remotely and perform various operations.
Almost all Trojans and worms need an access to network, because they have to send data out to the hacker. Only the useful data are sent to the attacker the Trojan accomplishes its mission. So it should be a good solution that we start from the aspect of traffic analysis and protocol analysis technology. We are going to detect the Trojan horse and worm with the help of a –network analyzer-Colasoft Capsa. Capsa is an easy-to-use and intuitive network analyzer, which provides enough information to help check if there is any Trojan activities in our network. In this article I’m going to show you how to spot a Trojan or worm.
5 solutions to find the trace of a Trojan or worm in LAN network:
Solution 1: The Summary Tab
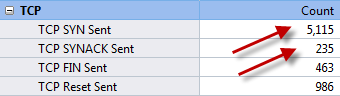
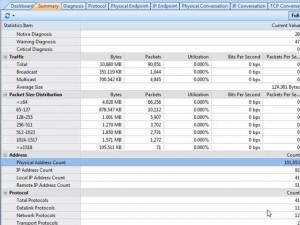
Concentrate on TCP packet summary. We should be alerted when TCP SYN Sent number is much larger than TCP SYN ACK Sent number. Generally the ratio of these two numbers approximately equals 1:1. Trojans and worms always send large amount of TCP SYN packet to the network and try to establish connections with other machines. When a connection established, they try to penetrate into the target machine.
Solution 2: IP Endpoint Tab
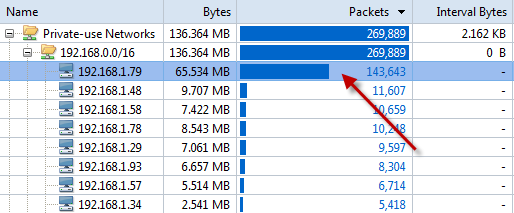
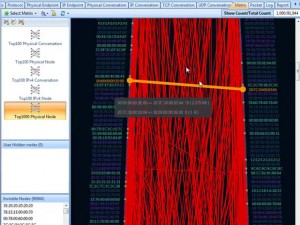
We can reorder the rows by clicking the column headers of the Packet Sent, Packet Received or IP conversation. Pay attention to the node with big statistics. They, however, might be BitTorrent downloading. But Trojans and worms definitely send out a large amount of packets.
Solution 3: The Log Tab
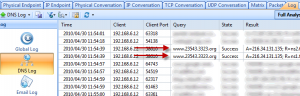
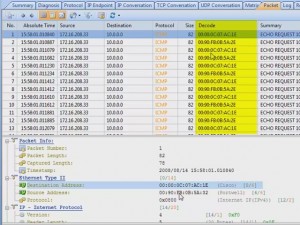
Focus on the DNS Log. We could make a list of target websites of Trojan horses by Google. For example, website like *****.3322.org. Furthermore, we can store the DNS log and analyze by using filters of the Trojans’ keywords.
Solution 4: Using Filters
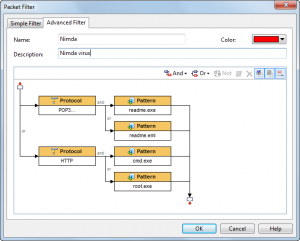
Build filters rules with patterns of some Trojans and worms. Until they send a packet out, we will get those Trojans’ and worms’ activities. This method has its drawback that it does nothing to a new Trojan or worm.
Solution 5: The TCP Conversation Tab & UDP Conversation Tab
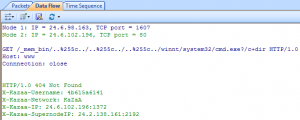
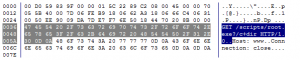
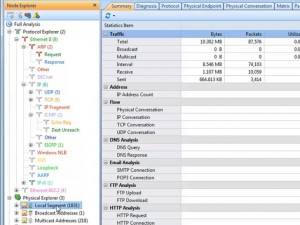
When Trojan or worm activities are found in our network, we can locate the machine’s IP address in the Node Explorer and then check its TCP Conversation or UDP Conversation. In TCP Conversation tab, we can read the reconstructed data of the communication in Data Flow sub tab, (the UDP Conversation is with the Data sub tab). Attentions have to be paid if the conversation is sending your system information.
Above are the featured tabs of Capsa network analyzer that we often use to detect network problems or bottlenecks. Moreover, we can spend some time to study what ports do the Trojans and worms like to use such as Executor:80, Ultors Trojan:1234. Then when we troubleshoot the network and make the analysis, we should pay attention to the node sending or receiving packets to and from these ports as well.