How to Baseline Network Throughput and Performance
What is network baseline?
Do you know what your normal network throughput volume is, what types of traffic are most used in your network? If you can’t answer these questions then you should baseline your network. Network baseline is very important to network management because the data will tell you what it’s like when everything goes all right.
To baseline your network, you need software or hardware to listen on your network or a particular device. Both Colasoft nChronos and Capsa can be used to accomplish this task. Both of them are used to listen into packet data of a wire and generate all kinds of statistics on the network. To baseline a network, you need to use them to monitor the network traffic long enough, because a wider time span presents a more real picture of network traffic pattern. The use of network baseline is listed as follows:
- Understand healthy network pattern and traffic trends.
- Evaluate network management policies compliance.
- Understand how the network resources are allocated.
- Accelerate to troubleshoot network issues, i.e. abnormal traffic and spam traffic, etc.
- Provide data on network and security management to support decision making.
- Provide history statistics on network upgrade.

How to baseline a network
Preparation
If you want to baseline a network, you can start from the tasks listed below:
1. Network diagram: draw the layout of the network structure, marking IP/MAC addresses, VLAN, and places of all routers, switches, firewalls, servers, management devices, and even the data flow directions.
2. Network management policy: helps you understand what services are allowed to run on the network, what traffic is forbidden, and what services should enjoy higher priority.
Scope & Objectives
When you are ready to start baselining your network, first you should think what to baseline because it’s hard or sometimes unnecessary to include all hosts, switches and routers of a big network into you baseline report. The suggestion is that you divide the network into several layers and only baseline the critical layers. For example, only baseline the services like ERP, Email, HTTP traffic and devices like core switches, routers and critical servers.
In addition to last point, different devices, hosts and links require different types of baseline data. For example, performance and security baseline is important to the servers, and network itself cares about throughput, utilization and types of traffic.
Collect baseline data
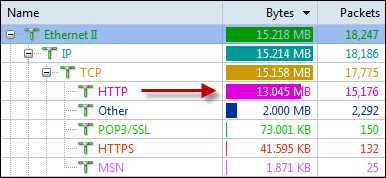
Generally speaking, a network baseline report contains these basic data: network utilization, traffic components, top protocols talkers, top hosts talkers, conversation statistics, address statistics, packet sizes, average packet length, and key server info, etc. Both nChronos and Capsa Network Analyzer provide these types of data (figure below).
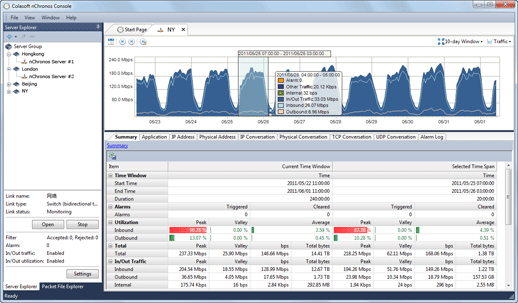
To use nChronos or Capsa to baseline a network, you need run nChronos or Capsa and use an excel sheet to record statistics over each specific time period. The following figure shows a typical Excel network benchmark table.
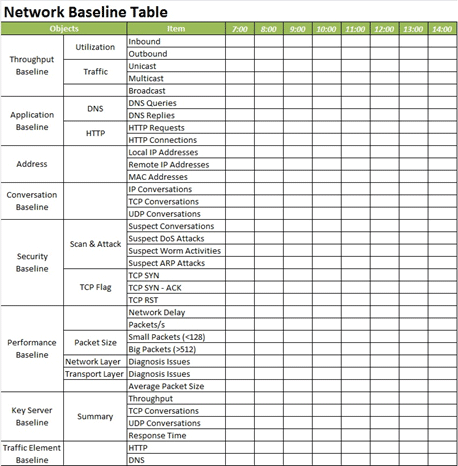
Then you can use formula to work out the max, min, and average value of each data type. And if you keep recording long enough, you get a much precise baseline statistics.
The use of network baseline data
The baseline data is often used when the network is reported to be running improperly. For example, when the network performance drops, you can compare the real-time datacollected from the analyzer with the baseline data to help you spot where the anomalies are.

Tips for network baselining
Update the baseline document in time
The baseline report is useful only when it provides accurate and up-to-date data. It requires that you update the data in time when there are any changes to the network. For example, when a new device is added, or a new application is implemented, the changes need to be marked on in the baseline report.
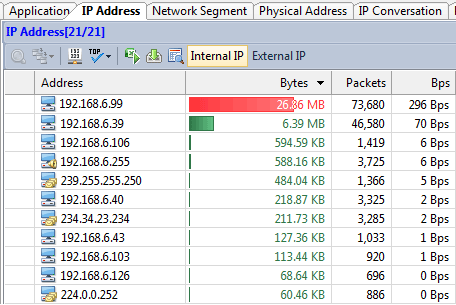
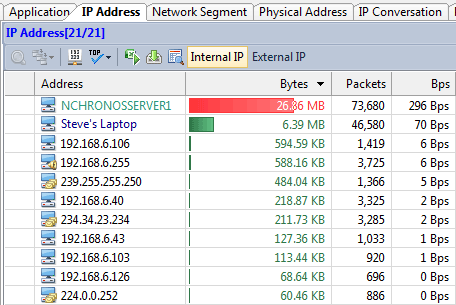
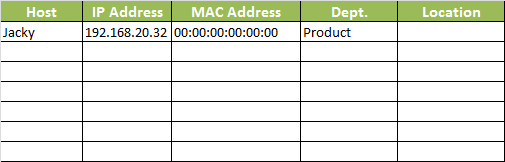
An IP/MAC database is necessary
If the network is full of desktops, laptops and switches, you should consider an IP/MAC database to record the user name and place of each individual IP and MAC address. It’s very helpful when you need figure out who is using the IP or MAC and where it is when you decide to give it an examination.
Baseline the critical devices only
Remember, you don’t have to maintain a baseline table which covers all your host computers, laptops, servers, switches, firewalls and routers. If you insist to do so, you’d better prepare enough time for it. You are suggested to only cover the mission-critical servers, such as email, web site, OA and CRM servers, and core switches and routers in your baseline report. And they’d better be organized in separate sheets to help you easily find what data you need.
Baseline over a long time period
It takes a long time to set up a network baseline because your network probably works in different patterns through Monday to Sunday. For example, on Monday morning, your email traffic could be higher than other days because there are lots of emails waiting to be processed after the weekend. On Friday afternoon after 4:00 PM, web traffic could be higher because some are browsing the web to find a place for the weekend. Therefore, your baseline report should cover the time period of a week at least, and you are suggested to extend to 2 ~ 4 weeks.
Keep baseline report easy to read
You should include all useful diagrams and illustrations in baseline report, the more the better, such as a network diagram, network policy, backups for switches and routers. The documents should be standardized with explanations and descriptions, especially for the technical terms. All of them are helpful when someone else is trying to access and read the documents.

from: colasoft.com
![]() to open the New Report dialog box:
to open the New Report dialog box: